Loureirin B
CAS No. 119425-90-0
Loureirin B( Loureirin B | LR-B | L B | LRB )
Catalog No. M17868 CAS No. 119425-90-0
Loureirin B can downregulate the expression of fibrosis-related molecules by regulating MMPs and TIMPs levels, inhibit scar fibroblast proliferation and suppress TGF-β1-induced fibrosis, during which TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway is likely involved.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 132 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 196 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 332 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 489 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 698 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLoureirin B
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLoureirin B can downregulate the expression of fibrosis-related molecules by regulating MMPs and TIMPs levels, inhibit scar fibroblast proliferation and suppress TGF-β1-induced fibrosis, during which TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway is likely involved.
-
DescriptionLoureirin B can downregulate the expression of fibrosis-related molecules by regulating MMPs and TIMPs levels, inhibit scar fibroblast proliferation and suppress TGF-β1-induced fibrosis, during which TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway is likely involved.
-
In VitroLoureirin B enhances the relative mRNA level of Pdx-1 and MafA. Loureirin B (1, 0.1, and 0.01?μM) increases insulin secretion in Ins-1 cells. Loureirin B (0.01?μM) almost causes no toxicity on cells. Loureirin B improves the level of expressions of MafA and Pdx-1 and ATP level. Loureirin B inhibits the KATP current but increases the [Ca2+]i level in Ins-1 cells. Loureirin B inhibits the expression of Col1 and FN, as well as the TGF-β1-mediated up regulation of p-JNK. Loureirin B also inhibits the up regulation of p-ERK that is induced by TGF-β1. Moreover, Loureirin B inhibits the contraction of TGF-β1-stimulated fibroblasts through the down regulation of p-ERK and p-JNK. However, Loureirin B does not suppress the up regulation of p-p38 that is induced by TGF-β1. Loureirin B downregulates both mRNA and protein levels of type I collagen, type III collagen and α-smooth muscle actin in a dose dependent manner in HS fibroblasts. Loureirin B also suppresses fibroblast proliferative activity and redistributes cell cycle, but does not affect cell apoptosis.
-
In VivoLoureirin B significantly improves the arrangement and deposition of collagen fibres, decreases protein levels of ColI, ColIII and α-SMA and suppresses myofibroblast differentiation and scar proliferative activity, in a rabbit ear scar model. Loureirin B effectively inhibits TGF-β1-induced upregulation of ColI, ColIII and α-SMA levels, myofibroblast differentiation and the activation of Smad2 and Smad3, in NS fibroblasts.
-
SynonymsLoureirin B | LR-B | L B | LRB
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number119425-90-0
-
Formula Weight316.35
-
Molecular FormulaC18H20O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 150 mg/mL; 474.16 mM
-
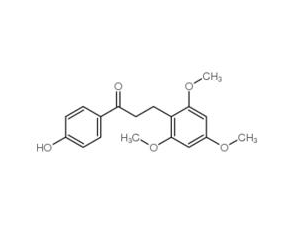
SMILESCOc1cc(c(c(c1)OC)CCC(=O)c1ccc(cc1)O)OC
-
Chemical Name1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)propan-1-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Bai X, et al. Loureirin B inhibits fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition in hypertrophic scar via TGF-β/Smad pathway. Exp Dermatol. 2015 May;24(5):355-60.
molnova catalog



related products
-
10-Formyl-5,8-dideaz...
10-Formyl-5,8-dideazafolic acid (CB3717) is a water-soluble analog of folic acid, also known as folate.
-
APE1-IN-1
APE1-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of purine/pyrimidine endonuclease 1 (APE1) that crosses the blood-brain barrier, exhibits potential antitumor activity, and enhances the cytotoxicity of the alkylating agent [methyl methanesulfonate] on cancer cells.
-
TFMB-(S)-2-HG
TFMB-(S)-2-HG (TFMB S 2 HG) is a highly effective inhibitor of TET2, the 5'-methylcytosine hydroxylase. Additionally, it significantly inhibits the EglN prolyl hydroxylases.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


